An important stage in the implementation of infrastructure projects is planning. This is preparatory work, during which the need for the planned project, economic, social and environmental benefits, expected results are determined, possible project implementation alternatives, costs, etc. are compared.
Following the international terminology, the initial phase of project justification is often called ” pre-feasibility study “. A detailed justification is called a feasibility study . However, sometimes both of these studies are classified as initial justification, while detailed justification is simply called “justification” or an investment project .
Feasibility studies and investment projects assess how one or another project is useful to society, calculate the likely benefits and costs of the project. For economically viable projects, funds spent on construction and project maintenance must pay for themselves within a specified project evaluation period. These studies, together with the project funding applications, are submitted to the EU structural funds and national institutions that finance the projects and are used in making decisions on whether or not to allocate the requested funds.
The content of a typical feasibility study or investment project includes:
• Project summary. It is designed so that it can be used separately from the feasibility study and evaluated as a separate document. The summary provides an overview of work administration, preparation and management information, indicates the project goals, briefly describes the project, needs analysis, alternatives, technologies, cost, presents evaluation results and conclusions;
• Information about the implementation of the project: name of the project, place of execution, organizers, beneficiaries, what categories the project is, according to which program it would be implemented, its compatibility with public policy and law is described, institutional and political aspects are presented;
• Project justification. This section presents the justification of the project in terms of essential socio-economic aspects and the analysis of the existing transport infrastructure;
• Project goals: the critical points of the current situation are identified, the need for the project is presented with goals and reasons. Technical indicators of the project are presented, their description (with alternatives and planned works);
• Environmental aspects. General data on economic activities, project developers and environmental impact assessment document developers are provided. The environmental situation at the site of the project preparation and the impact of the planned activities on the environment are named. An environmental impact assessment is carried out and a description of preventive measures is prepared;
• Project implementation plan: a project preparation, implementation and management schedule and project implementation schedule are drawn up;
• Social impact: it describes the impact the implemented project will have on the users of the facility, its influence on the population living in the zone and performing various economic activities;
• Financial analysis: financial indicators are calculated;
• Economic analysis: the economic indicators of the project are calculated;
• Sensitivity and risk analysis.
Risk evaluation
Palisade @Risk 6.2 Industrial software is used for risk assessment of infrastructure projects. The risk assessment method used by this software is Monte Carlo simulation. The simulation is performed after evaluating the factors influencing the project risk, their possible values, and the possible distribution of values. The program has the ability to describe various types of variable value distributions (normal, triangular, binomial, Poisson and others). The result of the risk assessment is the economic estimates of the infrastructure project and the predicted probabilistic distribution of their values.
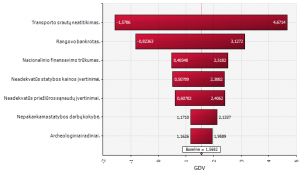
Below is a fragment (example) of the results of the risk assessment:

Probability distribution of the value of the internal rate of return

Variables affecting the net present value and the extent of their influence
 Current distribution of traffic flows in
Current distribution of traffic flows in